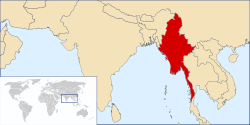
בורמה – מיאנמר – Burma Myanmar
בורמה (מיאנמר) 

The first kyat circulated in Burma between 1852 and 1889. The Royal Mint was established in Mandalay by Mindon, the second last king of Burma. Silver coins in denominations of 1 pe, 1 mu (2pe), 1 mat (4pe), 5 mus (10pe), and 1 kyat, and gold coins were minted in denominations of 1 pe and 1 mu.. The obverse side of the first coins were stamped with the Royal Peacock Seal, and the reverse displayed the date and denomination. Towards the end of the first kyat, in the 1860s and 1870s, lead ⅛ and ¼ pya coins were minted, along with ½ pe and 2 pya coins minted in copper, brass, tin, and iron. Gold 1 pe, 2 ½ mu, and 1 kyat coins were minted between 1866, followed by gold 5 mu coins in 1878The Myanma kyat (Burmese: the currency of Myanmar (Burma). It is subdivided into 100 pya. The kyat was initially introduced in 1852, but was replaced by the Indian rupee in 1889. From 1943 to 1945, it was used again before being replaced by the Burmese rupee. The current kyat has been circulating since 1952. . From 1942 to 1945, the Empire of Japan occupied Myanmar . The third, and current kyat was introduced on July 1, 1952 . In 1952, bronze 1 pya, cupronickel 5 pya, 10 pya, 25 pya, 50 pya, and 1 kyat coins were issued. In 1966, the coins denominated in pyas became composed of aluminum. The 1 pya coins were last minted in 1966, the 5 pya coin in 1987, and the 10, 25, and 50 pya coins in 1991. In 1999, a new series of Myanma coinage was introduced, which consisted of a bronze 1 kyat, brass 5 and 10 kyat, and cupronickel 50 and 100 kyat coins
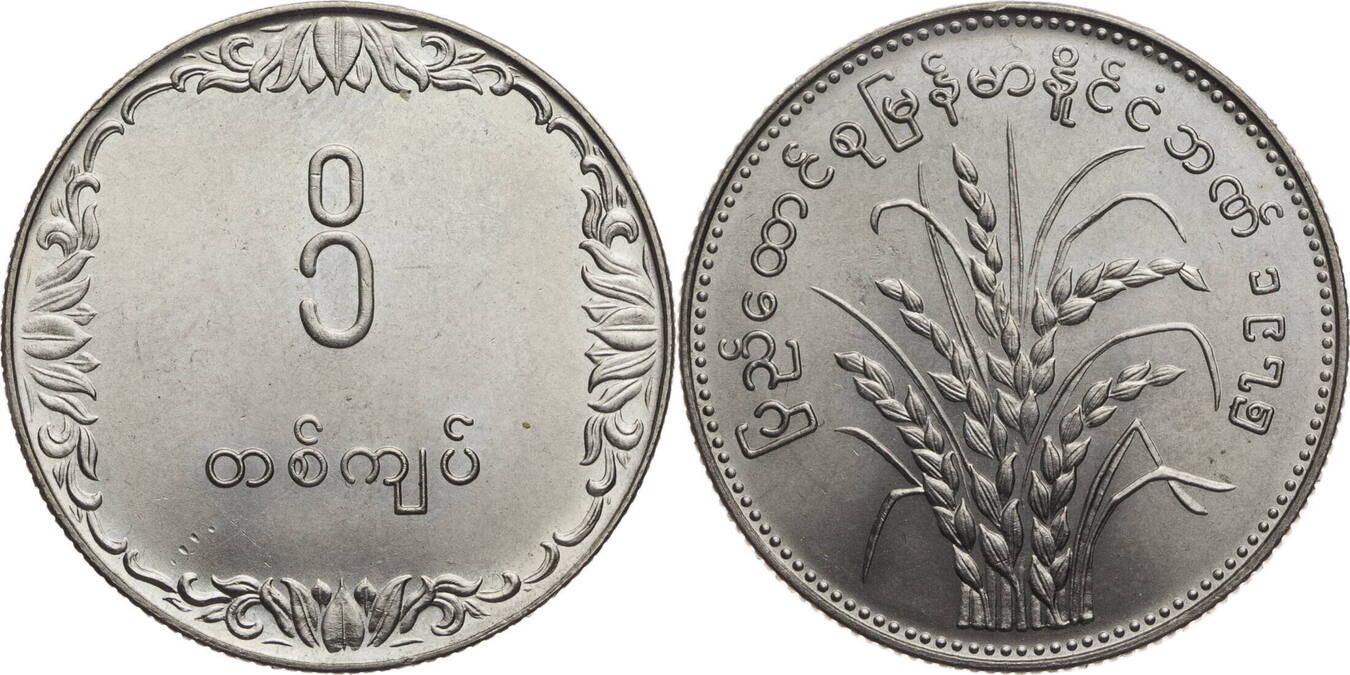
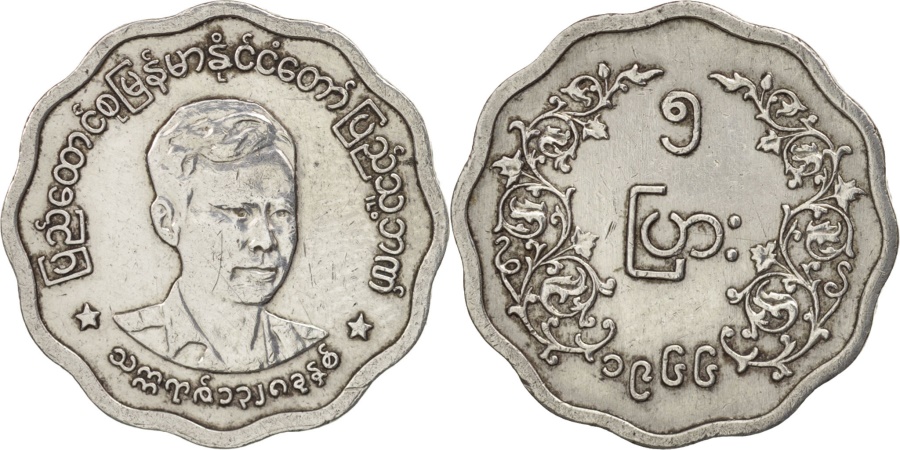
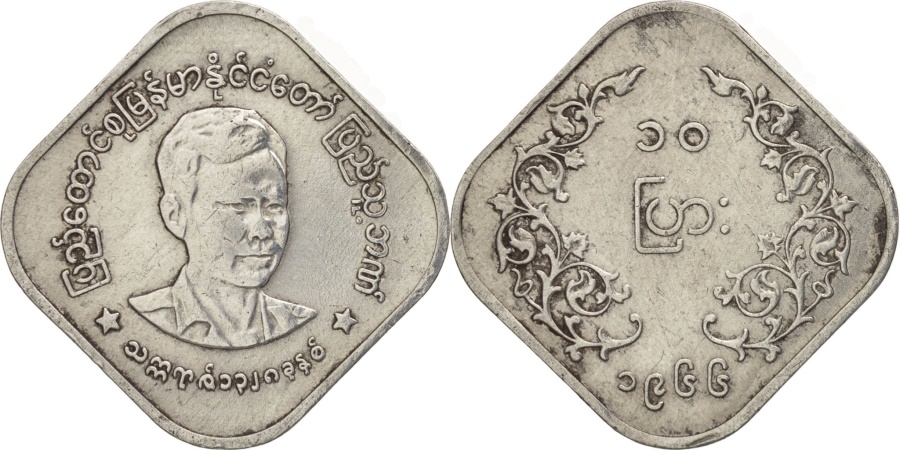
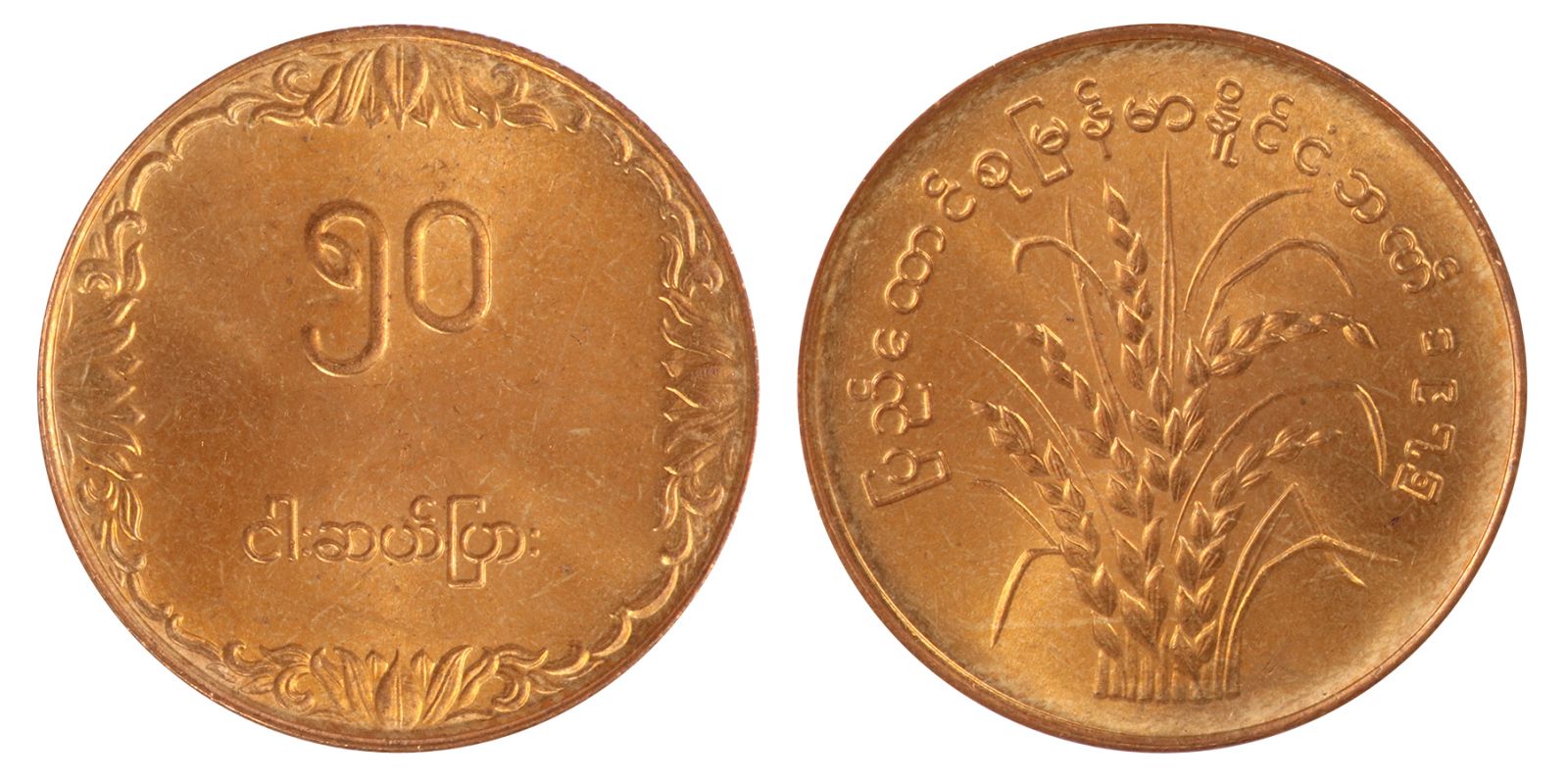










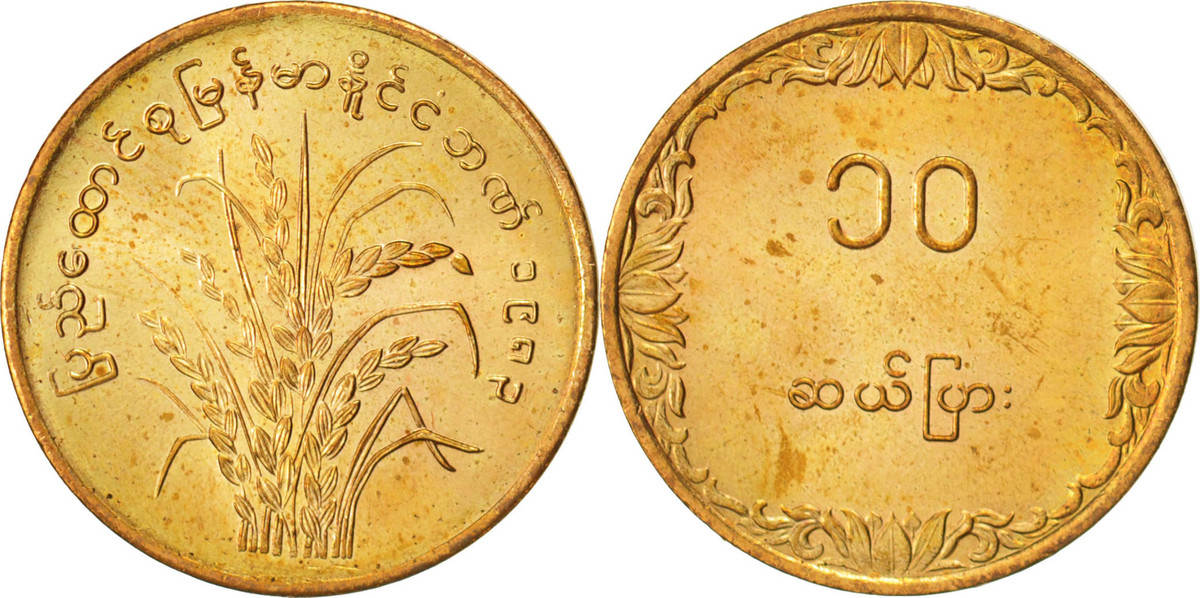
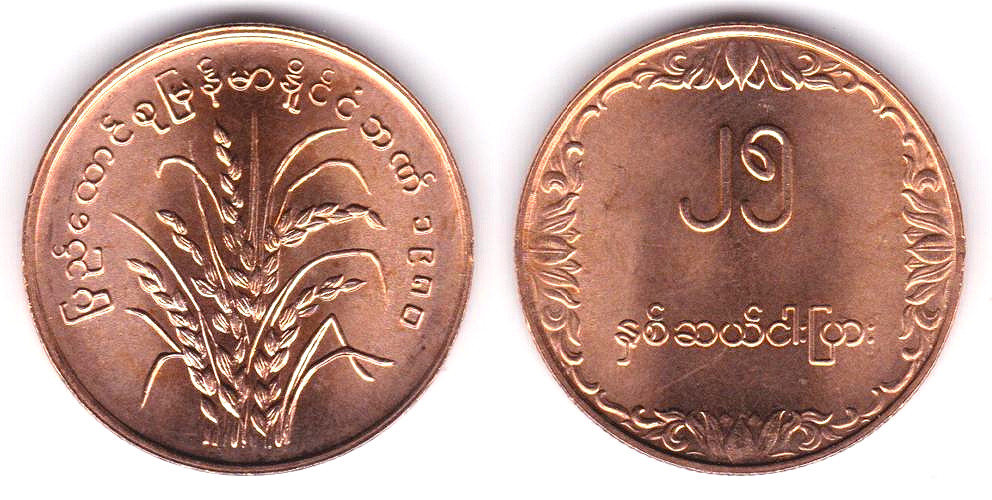












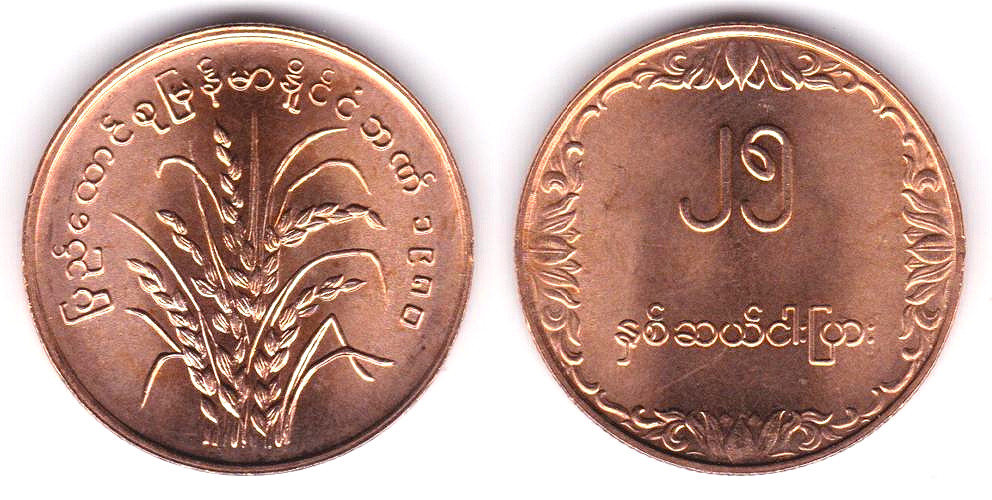


בורמה 


_donatedth_f.jpg)
_donatedth_b.jpg)
_donatedoy_f.jpg)
_donated_b.jpg)
מיאנמר בירמני 

_ASEAN_svg.png)



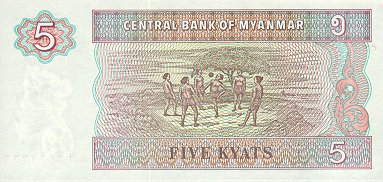


_donatedoy_f.jpg)
_donatedoy_b.jpg)
_donatedoy_f.jpg)
_donatedoy_b.jpg)
_donatedoy_b.jpg)
_donatedoy_f.jpg)